Microsoft: Raspberry Robin worm already infected hundreds of networks
Security Affairs
JULY 3, 2022
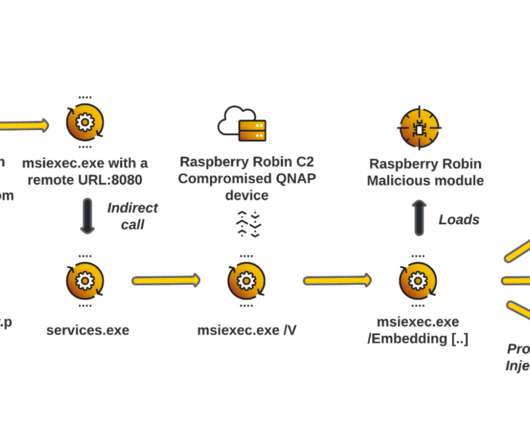
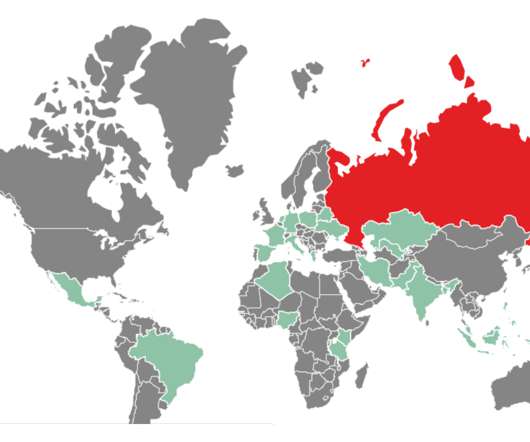
The malware was first spotted in September 2021, the experts observed Raspberry Robin targeting organizations in the technology and manufacturing industries. In the example below, q:erpbirel.yax deciphers to d:recovery.lnk.”. The malware uses TOR exit nodes as a backup C2 infrastructure. exe to execute a malicious command.
















Let's personalize your content