Strong Encryption Explained: 6 Encryption Best Practices
eSecurity Planet
JANUARY 5, 2024
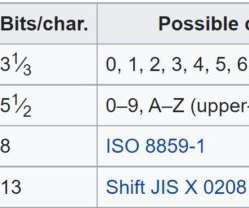
Strong encryption protects data securely from unauthorized access, but the specific algorithms that qualify as strong encryption change over time as computing power increases and researchers develop new ways to break encryption. What Makes an Encryption Algorithm Strong?


























Let's personalize your content