Examples and uses of GIS
IBM Big Data Hub
DECEMBER 18, 2023
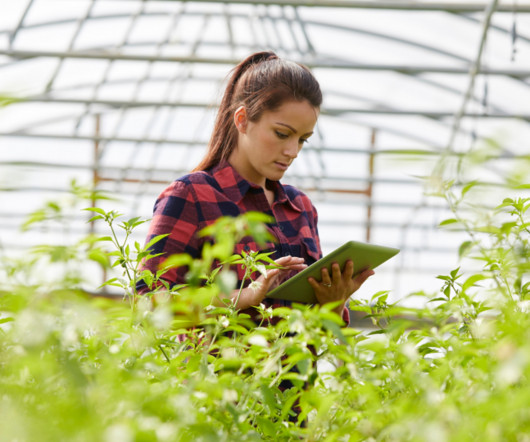
GIS perform spatial analysis of geospatial datasets—consisting of vector data (points, lines and polygons) and raster data (cells with spatial information)—to produce connected visualizations. Agriculture GIS technology makes productive, sustainable farming possible by providing accurate, comprehensive data.








Let's personalize your content