Cloud workload protection (CWP) is the process of monitoring and securing cloud workloads from threats, vulnerabilities, and unwanted access, and is typically accomplished via Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP).
Cloud workloads are everything needed to run an application in the cloud, such as databases, containerized environments, and the application itself. As cloud computing upends traditional perimeter models of cybersecurity, new cloud security models have emerged, and CWPP was one of the first to appear back in 2010.
We’ll cover how cloud workload protection works, its relation to other cloud security solutions, and considerations and options for those evaluating cloud workload security options.
Also read: CSPM vs CWPP vs CIEM vs CNAPP | What’s the Difference?
Jump ahead to:
- How Cloud Workload Protection (CWP) Works
- Top 5 CWP Threats
- Workload Protection vs Application Security
- What Are the Benefits of Cloud Workload Protection?
- What Are the Challenges of Cloud Workload Protection?
- Utilizing Cloud Workload Protection Platforms
- Bottom Line: Strengthen Cloud Resilience with Advanced Workload Protection
How Cloud Workload Protection (CWP) Works
A Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) protects cloud workloads from malware, ransomware, distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, cloud misconfigurations, insider threats, and data breaches. While cloud service providers (CSPs) offer their own native security, CWPP offers an additional layer of customized protection and management to fit the demands of workloads. It provides full cloud security management, reducing risks and protecting assets. It handles cloud security risks that cloud service providers don’t, such as misconfigurations and user connection vulnerabilities. CWPP implements the following approaches to prevent, detect, and respond to security events:
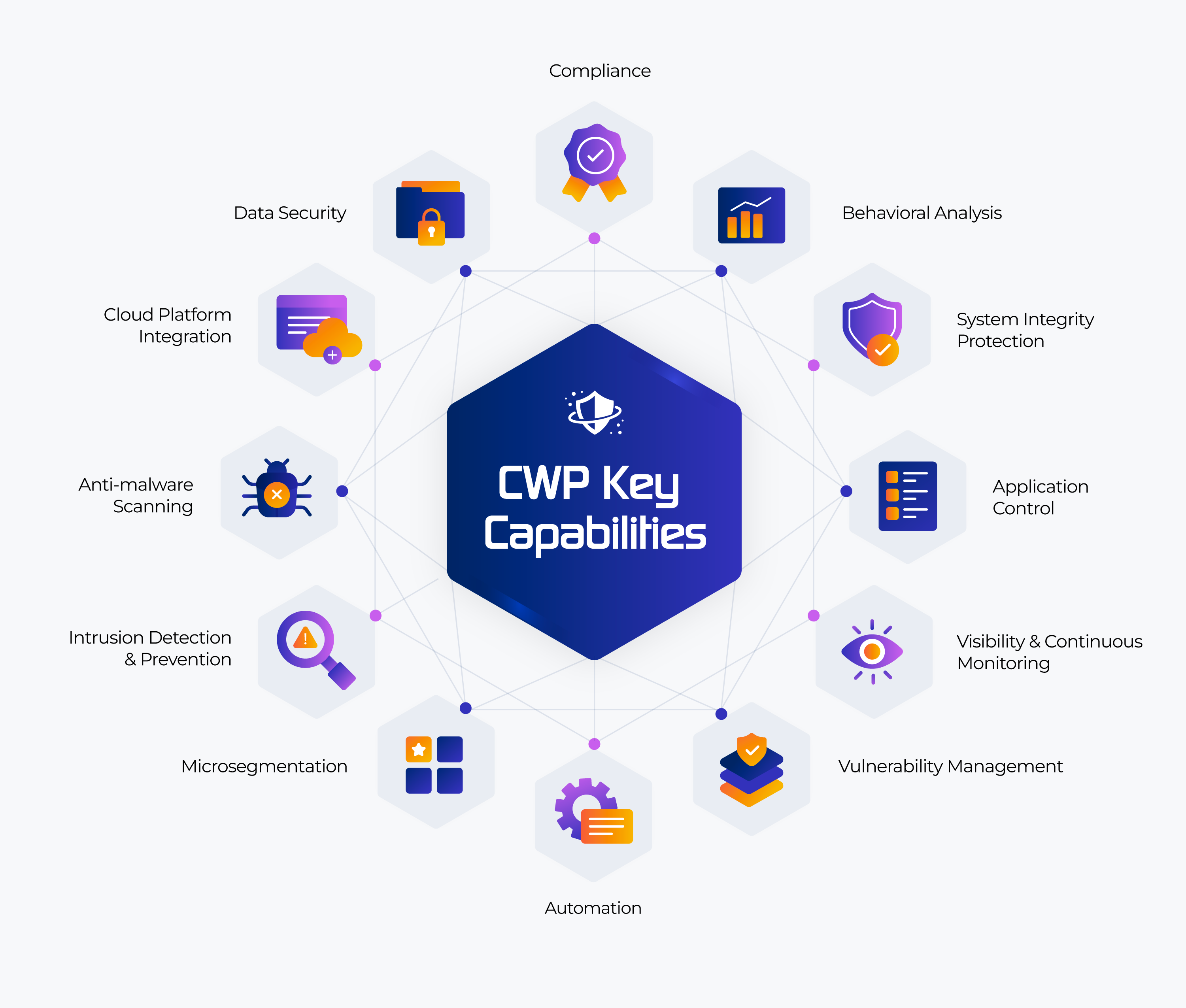
Visibility and Continuous Monitoring
CWPP provides full system supervision, monitoring PCs, virtual machines, containers, and serverless configurations. This necessitates real-time monitoring of cloud workload behavior, which is a critical component of CWP. Workload settings, software inventories, network connections, and user access privileges are all visible using CWPP tools. This enables security teams to detect abnormalities, illegal actions, and security risks more quickly, improving reaction and risk mitigation capabilities.
Unusual patterns prompt observations and further investigation. Anomaly detection systems recognize anomalous behavior by analyzing past data and trends. For example, if a web server unexpectedly connects with an unknown IP address, an alert may be triggered. After establishing a baseline of usual behavior, deviations from the norm indicate possible security vulnerabilities. CWP examines logs from workload components such as programs, operating systems, and network devices. This proactive strategy enables CWP to recognize and respond to abnormalities before they grow into serious concerns.
Vulnerability Management
Cloud workloads are frequently scanned by CWPPs for known OS, app, and software vulnerabilities and other issues. These scans might be planned or triggered by changes in the environment. After identifying vulnerabilities, CWPPs evaluate their impact, exploit possibilities, and commercial impacts. Critical vulnerabilities are given immediate treatment. Patches or upgrades are recommended by CWPPs, allowing for automatic patch management and secure setups.
CWPPs maintain vulnerability databases that are routinely updated to reflect current threat intelligence. New vulnerabilities cause security teams to get real-time notifications. Stakeholders, auditors, and compliance staff are provided with detailed vulnerability reports. Within CWPPs, organizations may customize vulnerability policies to correspond with risk tolerance and compliance, allowing for individualized assessments and responses.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention
CWPP protects against unwanted access attempts in real time by recognizing and stopping them. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) are critical components of cloud workload security because they detect and prevent unwanted access and harmful activity.
IDPS recognizes and blocks common threats such as specific malware or intrusion attempts by utilizing a database of known attack patterns (signatures). Anomaly-based detection in IDPS, like continuous monitoring, examines traffic patterns and user behavior for anomalies that may suggest an attack. IDPS can respond to recognized hazards by blocking or diverting suspicious traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
Microsegmentation
The microsegmentation strategy used by CWP platforms divides a cloud environment into smaller, isolated segments, each with its own set of security protections. By reducing lateral threat movement across cloud workloads, this method results in greater security.
Cloud resources are network-isolated from one another, making illicit communication between workloads impossible. Each task segment can have its own set of access constraints, allowing enterprises to limit interaction with only the resources necessary. Microsegmentation is consistent with the zero trust concept, which requires continuous reverification of connections. By separating different parts of your system from one another, CWPP helps to prevent the spread of attacks. If one component fails, the others can keep working properly.
Behavioral Analysis
Behavioral analysis, a machine learning-driven approach, assesses cloud workload and app activity to identify possible security issues. CWPP creates a baseline of behavior and alerts users when anomalous shifts occur. A sudden huge data transfer to an external server, for example, might suggest data exfiltration. Machine learning models use historical data to identify typical cloud workload and app behavior. Anomalies such as unexpected network activity or illegal data access prompt alarms, allowing for rapid examination and response.
System Integrity Protection
CWPP protects fundamental system components against tampering, prohibiting attackers from interfering with critical components. It helps security teams detect and mitigate breaches, as well as conduct forensic investigation and collect evidence. CWPPs prevent unwanted modifications to files, configurations, and software by employing approaches such as hash-based verification, file integrity monitoring, configuration management, and automated remediation. Some CWPPs support the “immutable infrastructure” approach, which considers components to be read-only. Updates create fresh instances, avoiding illegal changes and ensuring quick recovery after a breach.
Application Control
CWPP manages application activity, thus reducing malware threats. Apps are separated into whitelisted (approved) and blacklisted (denied) lists. Only approved applications are allowed to operate, and they are vetted using threat intelligence, while suspicious applications are automatically prohibited depending on their reputation score. The behavior method detects new threats that signatures miss. Sandbox applications are used by some CWPPs for isolated monitoring. Admins can create granular policies that specify which apps, conditions, and permissions are permitted. To prevent attack, CWPPs automatically block, isolate, or eliminate dangerous programs.
Malware Detection and Prevention
CWPPs scan cloud workloads on a regular basis, employing signatures and heuristics to eliminate viruses, worms, trojans, and threats. They check files for known malware signatures. Files, memory, registries, and processes are all covered by deep scans. Integrating with SIEM allows for the centralization of discovered malware and events. When malware and threats are discovered, CWPP solutions automate measures such as isolating files and computers, limiting communication, and alerting administrators.
Cloud Platform Integration
Cloud providers offer APIs that allow third-party tools such as CWPPs to interface with and manage cloud resources. CWPPs use APIs to acquire information, apply policies, and act on resources. They interface directly with certain cloud services. AWS-based CWPPs, for example, interface with Amazon EC2, S3, and Lambda for increased security inside those services. APIs assist CWPPs in discovering and inventorying resources like virtual machines, containers, storage, and serverless operations. APIs are used to directly apply security rules.
With automated deployment, CWPP makes setup easier. To impose access controls, it connects with security groups, firewalls, and network solutions. Logs are collected from several services to provide a full picture. Some CWPPs enable different cloud providers, guaranteeing consistent security across a variety of settings, making them ideal for multi-cloud strategies.
Data Security
Protection of data is a crucial function of any CWP platform. It should include encryption, DLP, and access management to prevent unauthorized access, exfiltration, or leaking. These safeguards protect data at rest and in transit, reducing the chance of a compromise.
CWPPs prioritize data security through encryption at rest and in transit. They provide encryption management solutions for databases, storage, and communications. Fine-grained access controls guarantee that only authorized people have access to data. Roles and permissions are handled through integration with identity management. DLP monitors and inhibits the illegal transfer of data and helps to stop insider threats. It searches for patterns, keywords, and formats before taking actions such as blocking or encrypting. Tokenization, or data masking, may be used by CWPPs to replace sensitive data with tokens. Actual data is securely kept elsewhere and can only be decrypted by authorized users. CWPPs can detect and categorize sensitive data and unauthorized access triggers alerts and actions. They guarantee secure workload configuration, permissions, services, and best practices.
Also read: Cloud Security Best Practices
Automation
CWPPs automate the detection and identification of security threats in real time. Anomalies initiate automatic reactions such as isolation, blocking, or notifications. Incidents cause preset actions to be taken, such as quarantining, restoring, or initiating response procedures. Vulnerabilities are also patched via automation. CWPP constantly enforces organization-defined security policies. For example, if a policy restricts ports, CWPP shuts unnecessary or insecure ones. Automation allows for resource scaling while maintaining control. It ensures 24/7 monitoring and response.
Compliance
CWPPs collect cloud data for compliance reporting to help demonstrate that an organization has proper controls. They audit, appraise, and report on security configurations. Policies that require specific compliance are defined in CWPPs and then enforced. They provide secure configuration templates that match controls to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. CWPPs create logs as evidence of compliance, monitoring changes and access. In case of violations, CWPPs can trigger alerts and notify users for quick action. Automated assessments monitor compliance on a regular basis and provide adherence results.
Top 5 CWP Threats

Cloud Workload Protection Platforms are well suited for addressing a range of cloud security risks:
Data Breaches
Data breaches involve illegal access to sensitive data within cloud workloads, leading to data loss and privacy risks. To avoid intrusions, CWP technologies prioritize encryption, access control, and data monitoring. Cloud workloads store critical information such as client data, financial and payment records, and company secrets and intellectual property.
Shared accountability is followed by CSPs; service providers safeguard infrastructure, while customers secure data and apps. Misconfigured cloud workloads may inadvertently disclose data. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities created by insecure settings, open ports, or APIs. Because clouds are frequently multi-tenant, a breach in one area might have an impact on others if not properly isolated.
Malware and Ransomware
Malware infections and ransomware attacks can cripple cloud workloads, propagate to associated workloads, causing the damage to escalate. Phishing and unpatched software or misconfigurations are common entry points. To combat these threats, CWP systems employ real-time scanning, behavioral analysis and automated response.
Insider Threats
Insider threats occur when authorized personnel, such as employees, contractors, or partners, abuse their access to cloud workloads by stealing or leaking sensitive data. Insiders may use their lawful access to avoid discovery and perhaps circumvent standard security controls. They are knowledgeable with systems and procedures, as well as weaknesses and insider information. This access allows them to target important data (proprietary, customer, and financial). Insiders can tamper with cloud workload data, jeopardizing operations and integrity. They might even disrupt, disclose information, or cause damage to cloud infrastructure. Insiders may also unintentionally fall victim to phishing, putting their credentials at risk and allowing attackers illegal access. Effective CWP techniques mitigate both external and internal risks.
Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations are serious and frequently underestimated risks in cloud environments that originate when cloud resources, applications, or services are not properly configured, creating vulnerabilities for exploitation. This results in data breaches, illegal access, service outages, and other security risks.
Misconfigurations often unintentionally expose sensitive data or resources to the public internet. As a result, attackers may get access to sensitive information. Misconfigurations can accidentally offer unauthorized users access, allowing attackers to compromise workloads or services. Weak authentication techniques might result in credentials that are easily guessable. Misconfigured APIs might expose critical functionality or data, allowing attackers to manipulate resources or get unauthorized data access. They allow for lateral mobility within cloud systems, potentially increasing the consequences. Non-compliance with regulatory standards can arise due to misconfigurations, and may lead to legal and financial consequences.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks target the availability and performance of cloud services, inundating them with malicious traffic or exploiting weaknesses to interrupt routine operations. While denial-of-service attacks may not directly jeopardize data confidentiality, they can have a major impact on an organization’s service delivery, resulting in financial losses, reputation harm, and operational interruptions. Attackers can take advantage of the scalability of cloud settings to launch more powerful, complicated DDoS operations that overburden cloud systems. Attackers may occasionally use DDoS assaults to divert attention from other actions like data theft or malware installation. CWP solutions include systems for detecting and mitigating such assaults.
Workload Protection vs Application Security

While they address different aspects of security, cloud workload protection and application security are interconnected and complementary within Cloud Workload Protection Platforms. While CWPP solutions focus on protecting cloud environments, application security is a deeper practice that ensures the applications themselves are secure, from secure development and coding to API and vulnerability management. Thus, application security and cloud workload protection are complementary practices that together provide a thorough defense against possible attacks.
Broader Cloud Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP) combine application security and cloud workload protection by bringing together a range of cloud security tools and functions, including cloud workload protection platforms, cloud security posture management (CSPM), cloud infrastructure entitlement management (CIEM), Infrastructure-as-Code (IAC) scanning and more to secure cloud workloads, applications, identity and access management, dev environments and more from threats and vulnerabilities.
What Are the Benefits of Cloud Workload Protection?
There are several advantages to implementing Cloud Workload Protection for businesses looking to increase the security of their cloud systems:
- Automation is frequently used in CWP systems to speed up security procedures. Automated response to threats and weaknesses guarantee prompt and reliable actions.
- CWP solutions offer an additional layer of protection that is specially created to shield cloud workloads from a variety of dangers. Critical data and applications are protected against cyberattacks as a result.
- Real-time monitoring of cloud workloads is provided by CWP systems, allowing for quick identification and reaction to security problems and helping to stave off data breaches.
- By minimizing the exposure of workloads to possible threats, CWP solutions lower the attack surface through strategies like microsegmentation and vulnerability management.
- Through the application of required security measures, CWP technologies assist enterprises in meeting compliance regulations.
- The scalability of cloud environments may be changed on the fly, and CWP solutions are made to accommodate this scalability. They can maintain constant security measures while easily adjusting to new workloads and resources.
- CWP platforms provide comprehensive insight into the security status of cloud workloads. Organizations may use this information to make educated decisions about security enhancements, ensuring that the most effective measures are implemented.
What Are the Challenges of Cloud Workload Protection?
Although Cloud Workload Protection has many advantages, it also has its own set of problems that businesses must address:
- Security management: Workloads in the cloud are dynamic, continuously scaling up or down in response to demand. It takes careful planning to keep security measures current and uniform throughout these changes.
- Shared responsibility: Following a shared responsibility paradigm, cloud service providers safeguard the infrastructure while the client is in charge of protecting their data and applications. This separation of duties can be confusing and can place a greater security burden on organizations than they realize.
- CI/CD integration: DevOps-adopting businesses strive for quick and frequent software releases. It might be difficult to effortlessly include security into this process without sacrificing some speed.
- False positives: Security settings that are too strict could result in false positives, causing unnecessary interventions and affecting operations.
- Cost: The most appropriate cloud security tools may be costly. Companies must reconcile security concerns with financial limitations.
Utilizing Cloud Workload Protection Platforms
These Cloud Workload Protection Platforms offer a range of methods and tools for preventing, identifying, and responding to security issues in cloud workloads. As businesses move and run their workloads in the cloud, they should be able to retain a solid security posture because of the visibility, control, and automation CWPP tools offer. Some notable Cloud Workload Protection Platforms are:
Illumio Core
Best for advanced microsegmentation capabilities
The sophisticated microsegmentation features of Illumio Core enables businesses to define fine-grained security boundaries across workloads and stop threats from moving laterally. Real-time threat detection, workload visibility, and adaptive security policies are further features of Illumio Core. It is a useful option for protecting cloud workloads because of its capacity to adapt to changing workloads and streamline visibility.
Pricing of Illumio Core units starts at $7,080 per 50 protected workloads and 25 ports annually.
Orca Security

Best for advanced cloud configuration capabilities
Orca Security’s agentless technique and extensive cloud visibility make it a leader in cloud configuration security. It offers continuous monitoring capabilities and broad insight across several cloud platforms. One of its distinguishing qualities is its capacity to identify vulnerabilities without the need for agents, guaranteeing low performance overhead and simplicity of setup.
Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto

Best for DevOps integration and container security
Palo Alto’s Prisma Cloud offers strong cloud security. It excels in integrating security with DevOps practices and guaranteeing container protection. Image scanning, runtime security, and compliance monitoring are all included in its container security features. Another layer of security is added by Prisma Cloud’s complete approach to cloud protection and data loss prevention.
Pricing starts at $9,000 annually per 100 Business Edition credits. You may also explore Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto’s pricing guide for further details.
Sophos Cloud Workload Protection

Best for its user-friendly interface
Organizations of all sizes may utilize Sophos Cloud Workload Protection thanks to its well-known user-friendly interface. It delivers complete security capabilities, such as visibility, encryption, and threat prevention. Its ability to effortlessly integrate with other security products and systems is one of its main advantages.
Trend Micro Deep Security

Best for hybrid cloud environments
With its host-based firewall, anti-malware, vulnerability management, and intrusion prevention capabilities, Trend Micro Deep Security thrives in hybrid cloud environments. It offers total workload security for deployments in both private and public clouds. Businesses looking for improved cloud security could use Trend Micro Deep Security due to its support for hybrid cloud architectures and strong security features.
See our in-depth guide to the Top Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
Bottom Line: Strengthen Cloud Resilience with Workload Protection
Cloud workloads are some of an organization’s most critical assets, and they require unique security controls to protect. Therefore, an effective cloud security plan should include Cloud Workload Protection as an integral piece of the system. CWPP provides a range of critical capabilities for safeguarding sensitive data, preventing unwanted access, and maintaining compliance, including microsegmentation, container security, and cloud configuration protection. Organizations can strengthen their cloud environments and successfully traverse the complex world of cloud computing while fending off possible attacks by knowing how CWP works, its advantages, problems, and the platforms available in the market.
Next: See the Top Cloud Security Companies








